Recently, Professor Chen Zihua's team from the Department of General Surgery at Xiangya Hospital of Central South University (CSU), Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Tumors, and National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders (XiangYa Hospital), in collaboration with Professor Zeng Wenbin’s team from Xiangya School of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Drug Research for Chronic Disease Diagnosis and Treatment, published the latest research findings as a paper titled “Precise visualization and ROS-dependent photodynamic therapy of colorectal cancer with a novel mitochondrial viscosity photosensitive fluorescent probe” in the international authoritative journal Biomaterials Research (IF=11.3).
How to diagnose and treat tumors efficiently and accurately is a long-standing issue and challenge in the clinical management of colorectal cancer (CRC). Oriented to the needs for precise killing of tumor cells and targeting the high viscosity characteristics of mitochondrial membranes in tumor cells, this original research skillfully combines viscosity-sensitive fluorescent molecules with mitochondrial charge targeting properties with ROS (singlet oxygen, 1O2)-dependent photodynamic therapy principles to design a multifunctional HTI fluorescent probe with high viscosity sensitivity and low biological toxicity. Tumor visualization is achieved in the model validation, and by controllable stimulation of excessive generation of ROS in the mitochondrial HTI aggregation region, the cell phospholipid membrane structure is disrupted through lipid peroxidation damage, so that colon cancer cells will be effectively inactivated. The ability of HTI to inhibit tumor growth has been successfully verified by adopting photodynamic therapy on the CRC-CDX model. The research findings have demonstrated the anti-tumor potential of HTI fluorescent probe from multiple perspectives and its application transformation value, providing novel ideas for visualized screening and adjuvant photodynamic therapy of CRC. It is expected to support medical professionals to efficiently diagnose and treat CRC in clinical practice, optimize the disease management process of CRC, and ultimately achieve a better prognosis for patients.
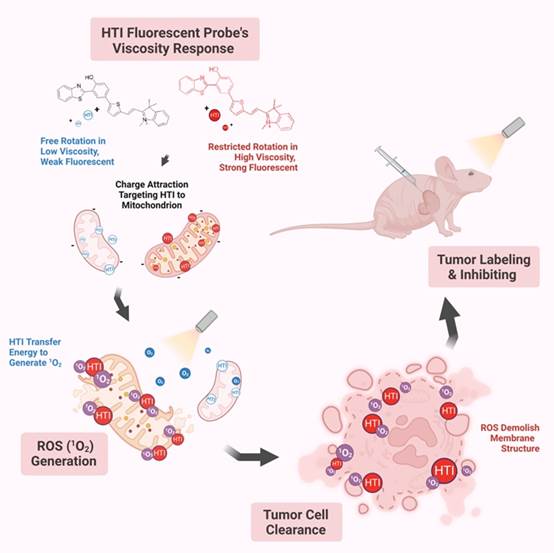
Mechanism chart for the research
CSU Xiangya Hospital is the affiliation of the first author and the corresponding author. Professor Chen Zihua and Professor Zeng Wenbin are the co-corresponding authors. Professor Chen Zihua's doctoral student Xiao Runsha from the Department of General Surgery at CSU Xiangya Hospital and Professor Zeng Wenbin's doctoral student Zheng Fan from CSU Xiangya School of Pharmaceutical Sciences are the co-first authors. The research has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province.
(First Reviewer: Yu Tao, Second Reviewer: Wang Xuan, Third Reviewer: Li Yin)
Source: Xiangya Hospital
Original article link: https://news.csu.edu.cn/info/1003/157371.htm